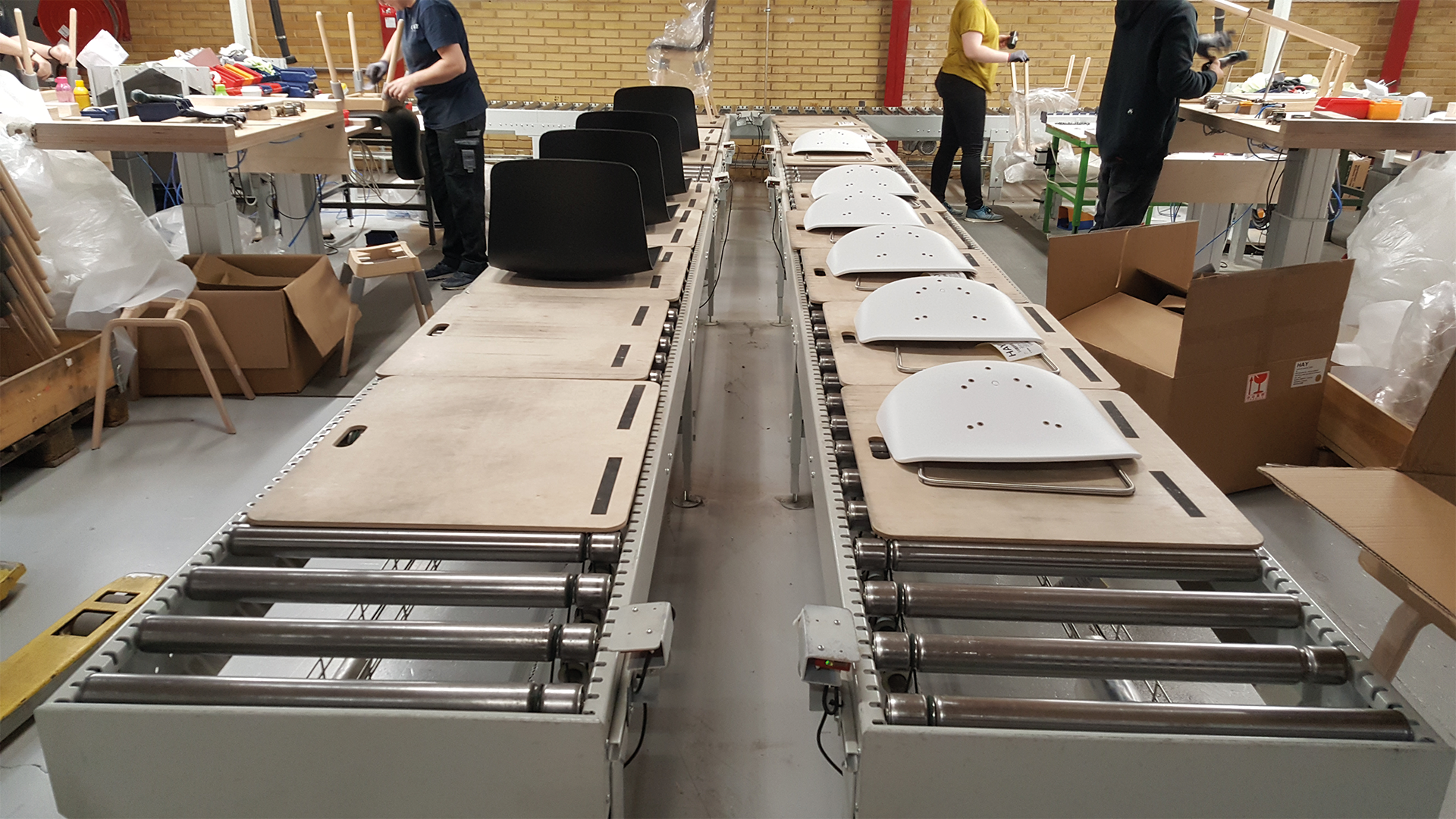

In 2016, Kvist Industries enhanced its chair production process with a custom transport solution from Q-System.
This system was designed to optimize workflow, improve ergonomics, and increase efficiency in assembling and packing chairs.
What We Delivered:
The automated transport system optimizes production flow while improving ergonomics for assembly staff.
- Manual assembly: Chairs are assembled on five rows of gravity roller conveyors.
- Automated transport: Once assembled, they are placed on transport plates and moved onto a driven roller conveyor leading to the packing area.
- Ergonomic handling: Along the way, a conveyor lowers the chairs to floor level, ensuring an ergonomic working height for packing.
- Packing and sealing: Packed chairs continue on the driven conveyor to a strap machine, where boxes are sealed and prepared for shipment to HAY’s central warehouse in Horsens.
- Efficient plate handling: Once a chair is removed for packing, its transport plate is automatically transferred to a stacking system, where full stacks are returned to production for reuse.
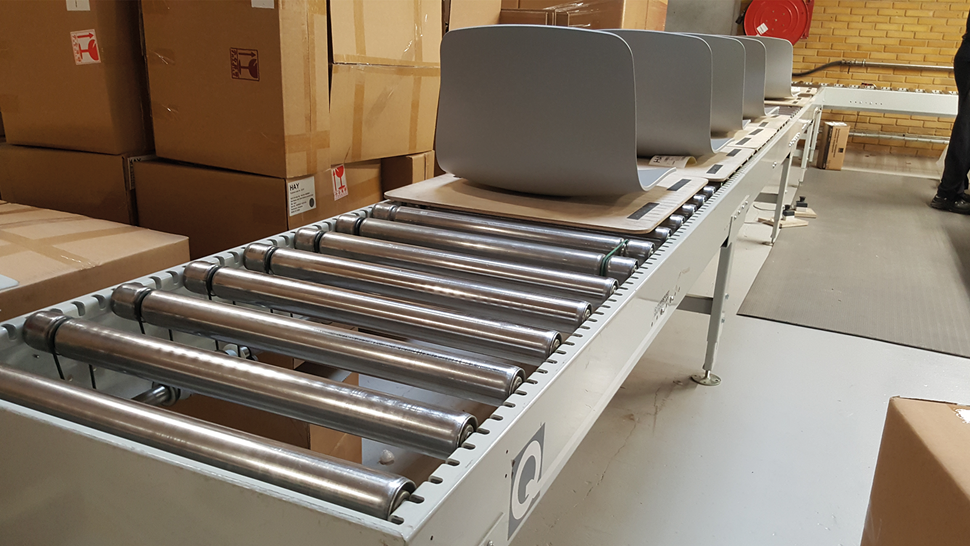



Machines used in this case:
- Driven conveyors
- Undriven conveyors
- Declining belt conveyor
- Angle transfer
- Side-sealing strapping machine
- Emergency stop button located at each operator's station
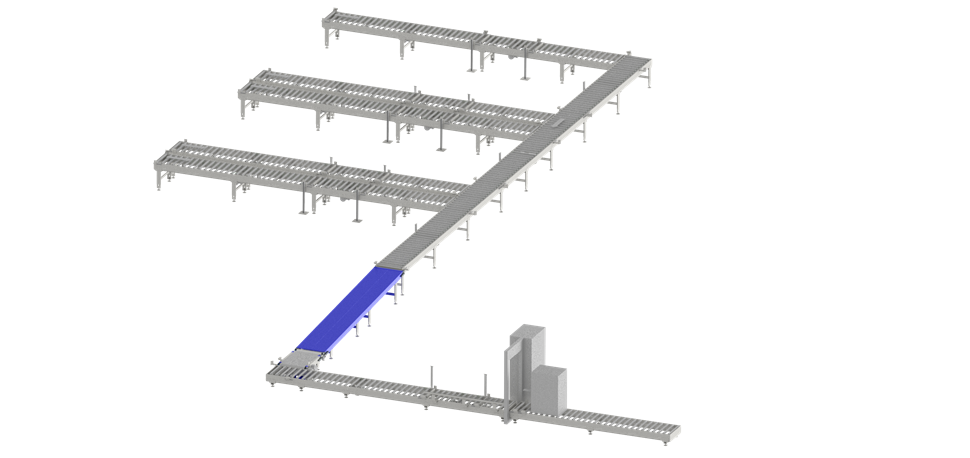
Step-by-Step Overview of the solution:
1. At the 5 Assembly Stations
When a box is placed at the end of the conveyor, it is automatically detected, and the first conveyor starts. The conveyor runs for a set period of time and stops at the separation stop.
2. Separation Stop Process
- Pressing Paddle Button 1 opens the separation stop, and the box moves to the next stop.
- Pressing Paddle Button 2 opens the separation stop again, and the box continues onto the extended conveyor. The box is then manually moved from the extended conveyor to the main conveyor.
3. Main Conveyor
The box is automatically detected at each of the 5 assembly stations, and the long conveyor starts. The box travels to the end before reaching the declining conveyor.
4. Declining Conveyor
The box is automatically detected, and the declining conveyor starts. The box is then angle-transferred automatically at position 5, and conveyor 6 begins.
5. Angle Conveyor with Strapping
The box is automatically detected, and the angle conveyor starts, provided it is not full. The box moves to the separation stop.
- Pressing Paddle Button 1 opens the separation stop, and the box moves forward for a set period of time.
- Pressing Paddle Button 2 restarts the conveyor, and the box moves towards the strapping station, where we control the strapping process.
6. Post-Strapping
After strapping is completed, the box moves to the extended conveyor if it is not full.
7. Queue Management
If there is a queue, the conveyors behind it will stop accordingly. If no boxes are detected for a set period of time, the conveyors will automatically stop to optimize energy consumption.













